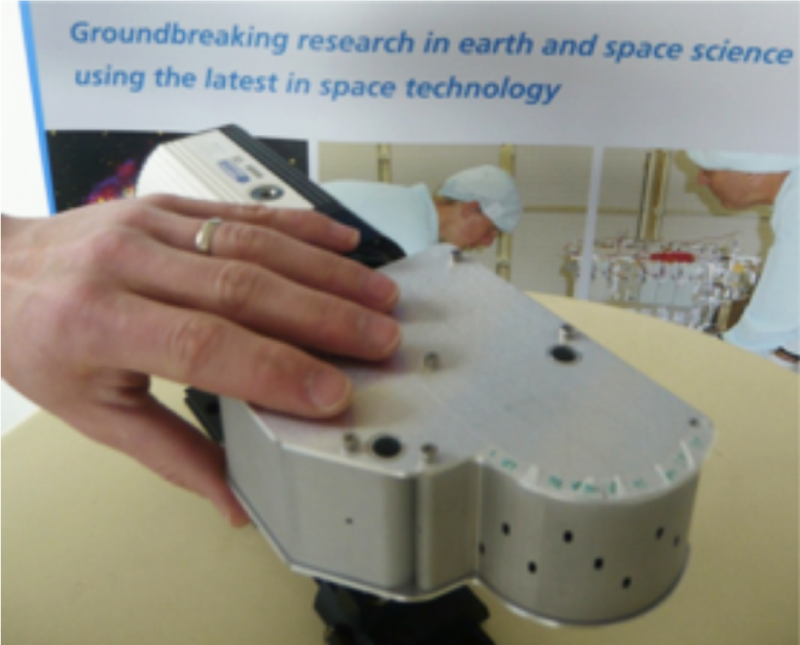
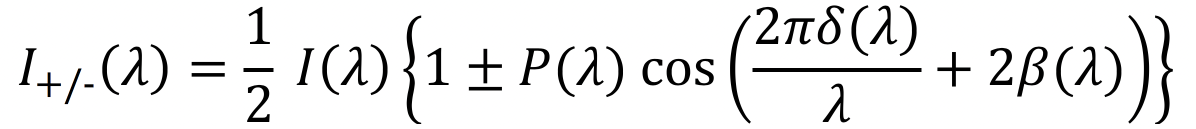SPEXone Polarimeter
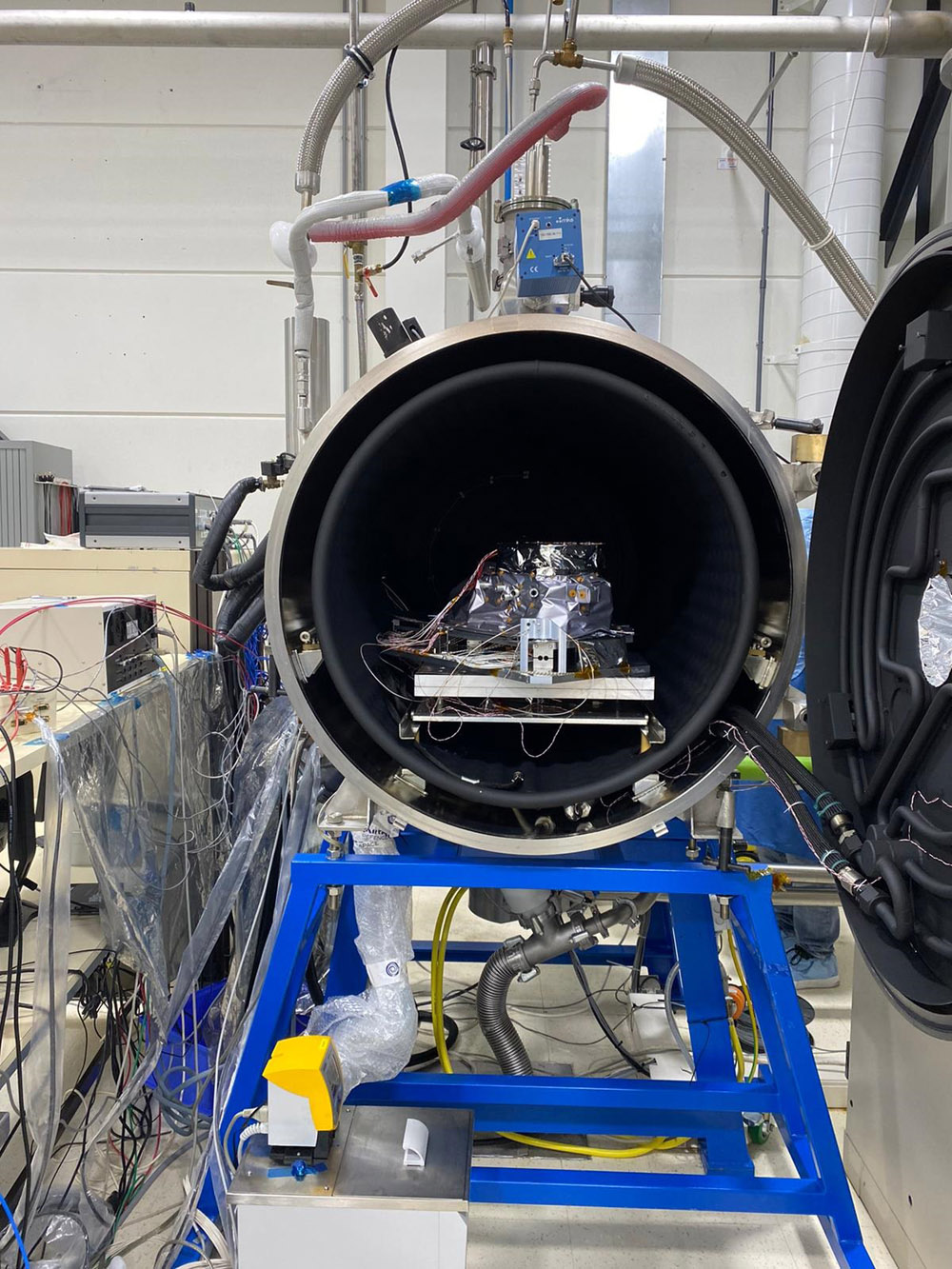
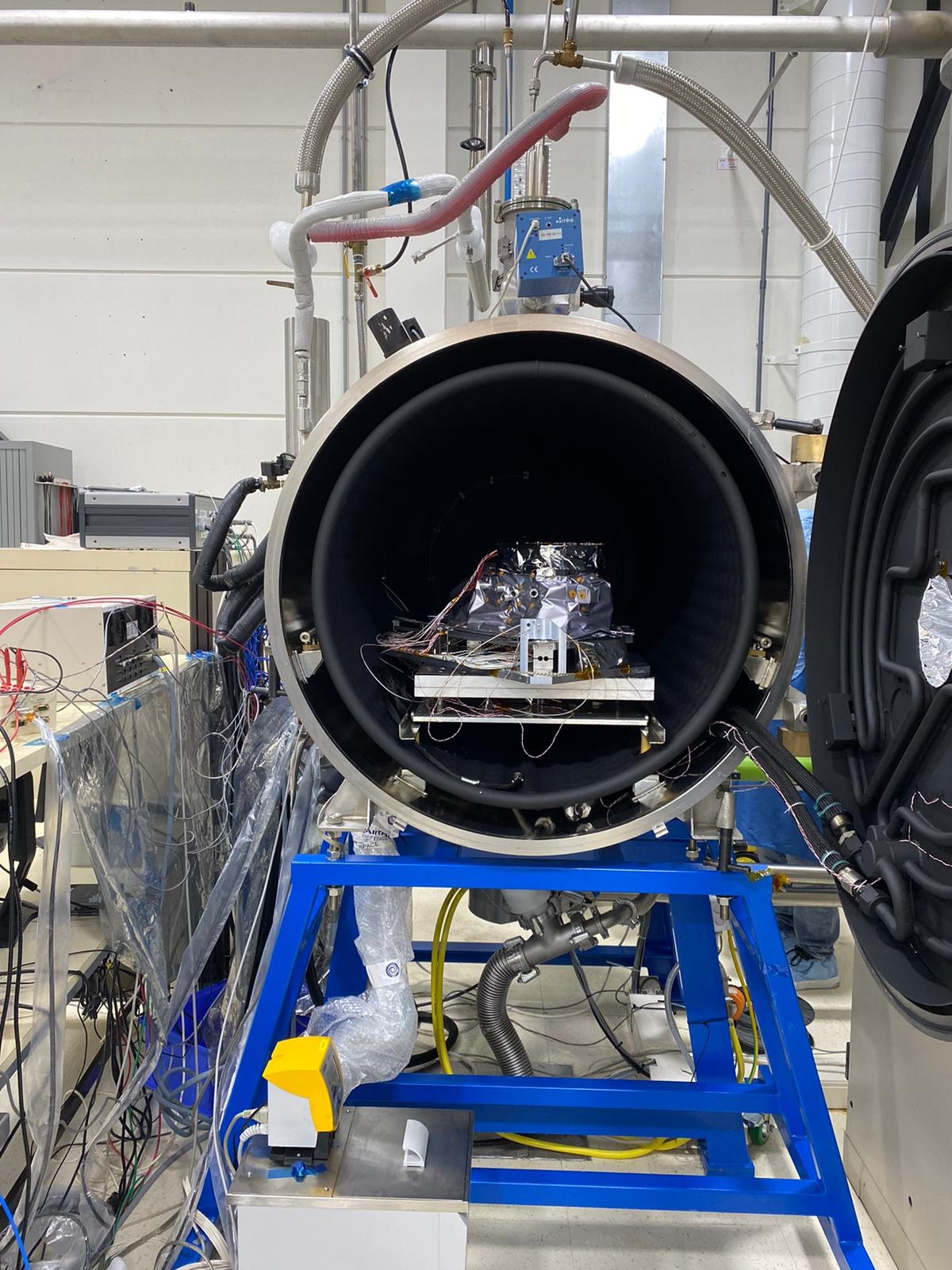
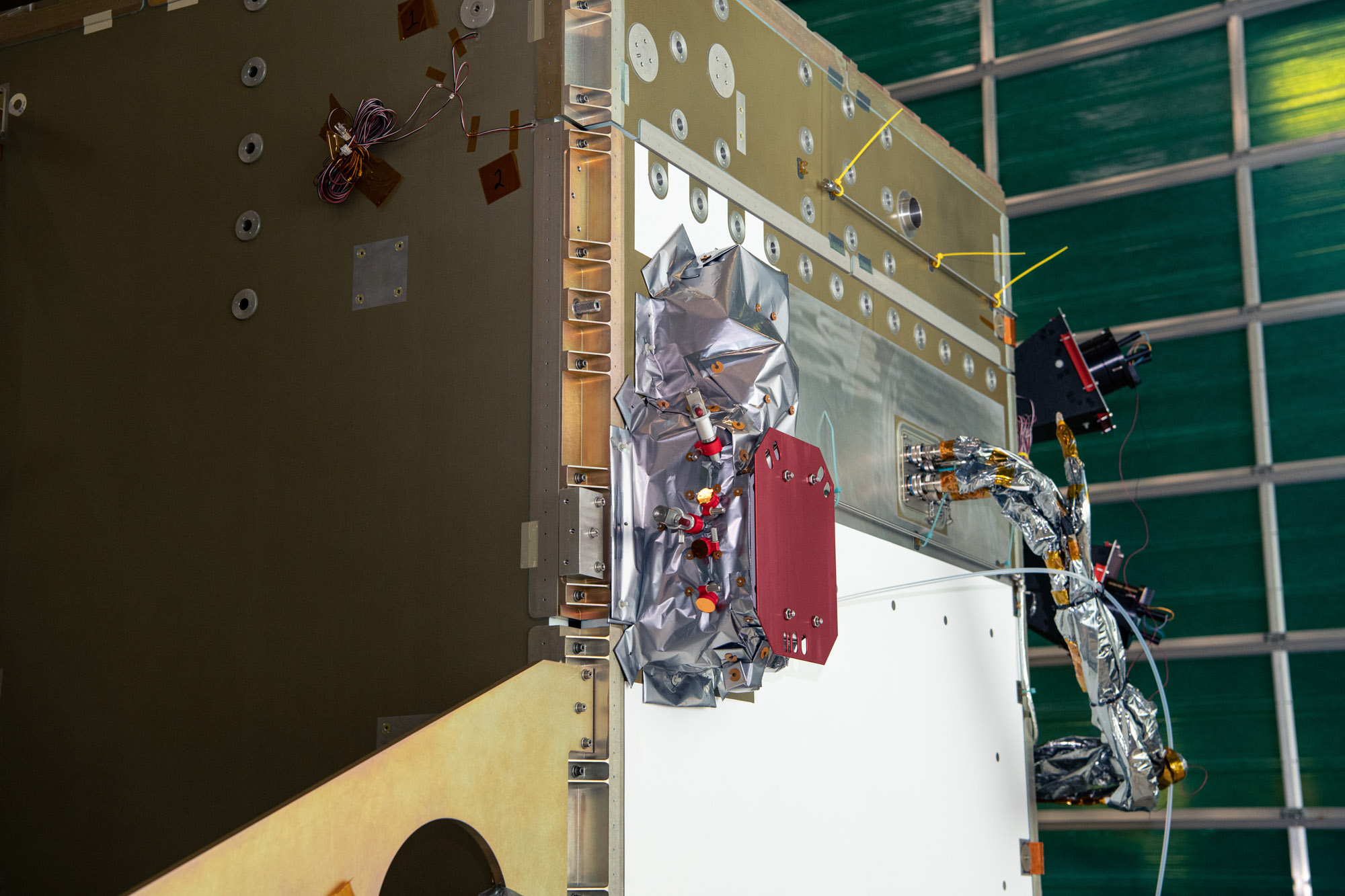
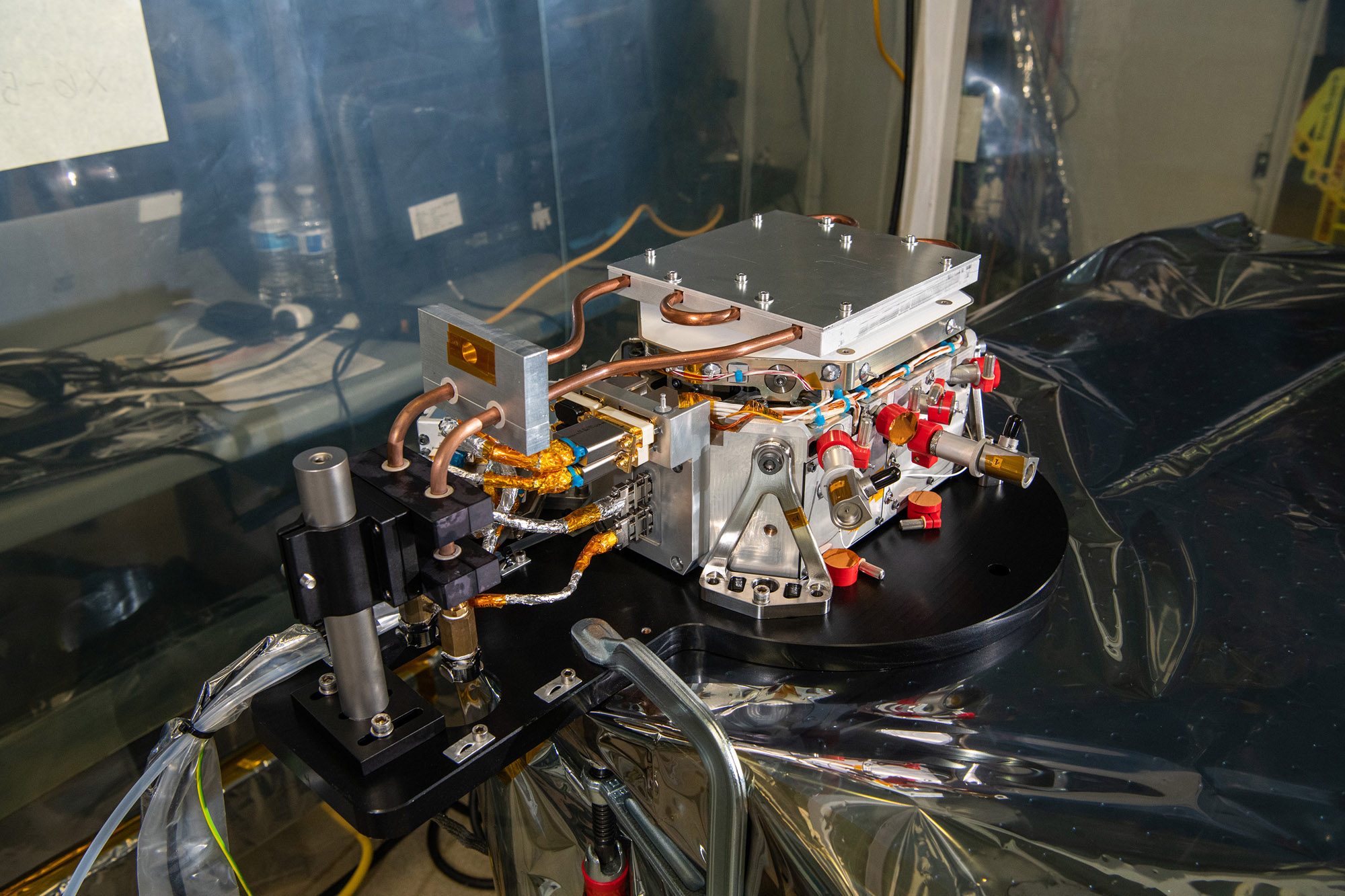
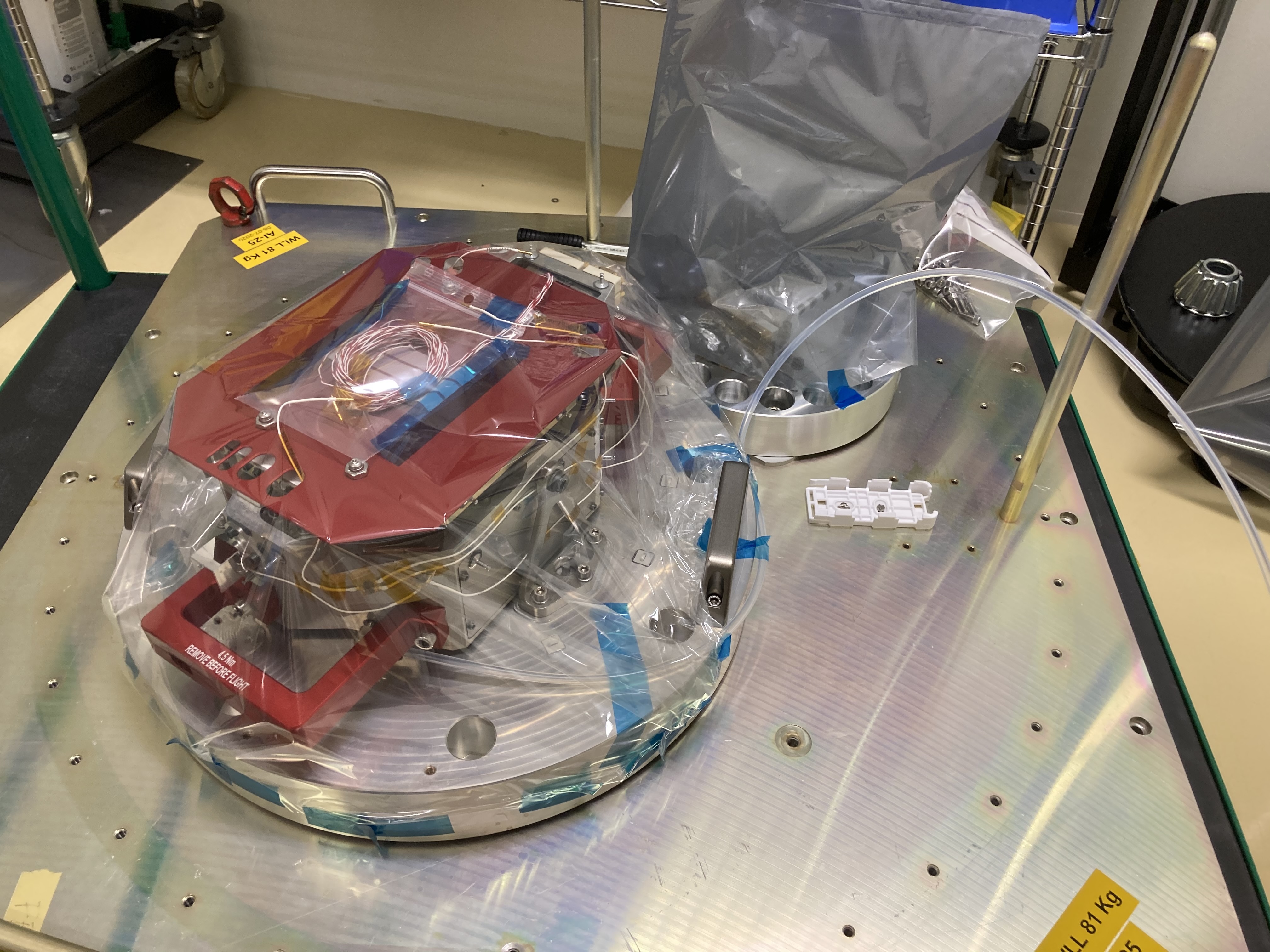
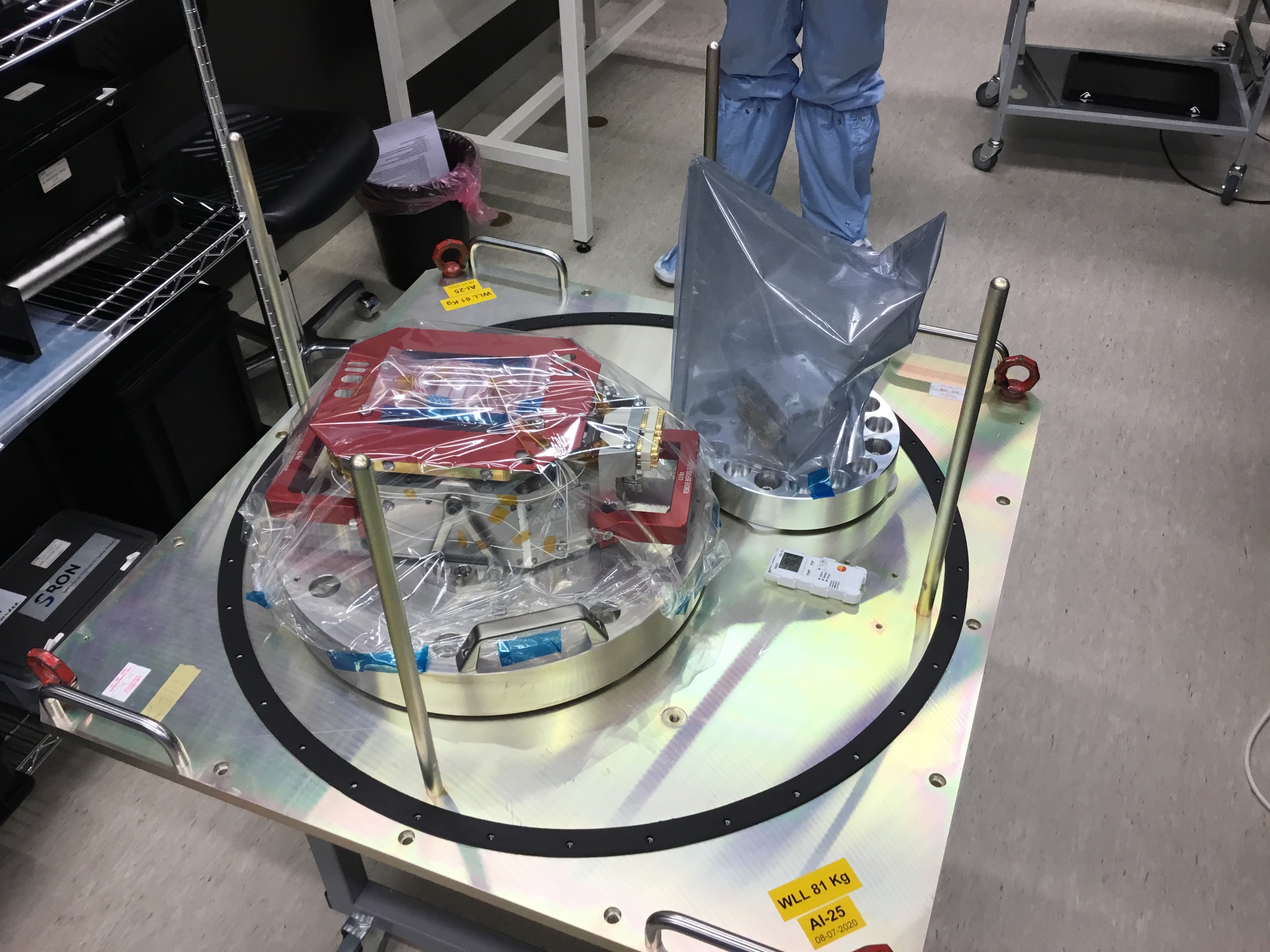
View images of SPEXone construction
PACE's SPEXone instrument is a multi-angle polarimeter. It measures the intensity, Degree of Linear Polarization (DoLP) and Angle of Linear Polarization (AoLP) of sunlight reflected back from Earth's atmosphere, land surface, and ocean. The focus of the SPEXone development is to achieve a very high accuracy of DoLP measurements, which facilitates accurate characterization of aerosols in the atmosphere.
Aerosols are small solid or liquid particles suspended in the air that affect climate directly through interaction with solar radiation. Aerosols affect climate indirectly by changing the micro- and macro-physical properties of clouds. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, aerosols are the largest source of error in quantifying the radiative forcing of climate change. SPEXone enables measurements of optical and micro-physical properties of aerosols with unprecedented detail and accuracy.
SPEXone was developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands (Airbus DS NL), supported by optical expertise from the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON, and Airbus DS NL.
SPEXone features:
Major steps in this development have been the development, characterization, and field-testing (ground-based) of a SPEX Prototype (originally designed for a Mars orbiter) and the "upgrade" of the SPEX prototype into a stand-alone instrument, SPEX airborne, for operating on the high-altitude (21 km or 13 mi) NASA ER-2 research aircraft.
The spectrometer of SPEXone is based on Dutch heritage with the Sentinel-5 precursor Tropomi instrument, its predecessor OMI, and the derived compact version Spectrolite.
Aerosols are small solid or liquid particles suspended in the air that affect climate directly through interaction with solar radiation. Aerosols affect climate indirectly by changing the micro- and macro-physical properties of clouds. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, aerosols are the largest source of error in quantifying the radiative forcing of climate change. SPEXone enables measurements of optical and micro-physical properties of aerosols with unprecedented detail and accuracy.
SPEXone was developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands (Airbus DS NL), supported by optical expertise from the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON, and Airbus DS NL.
SPEXone features:
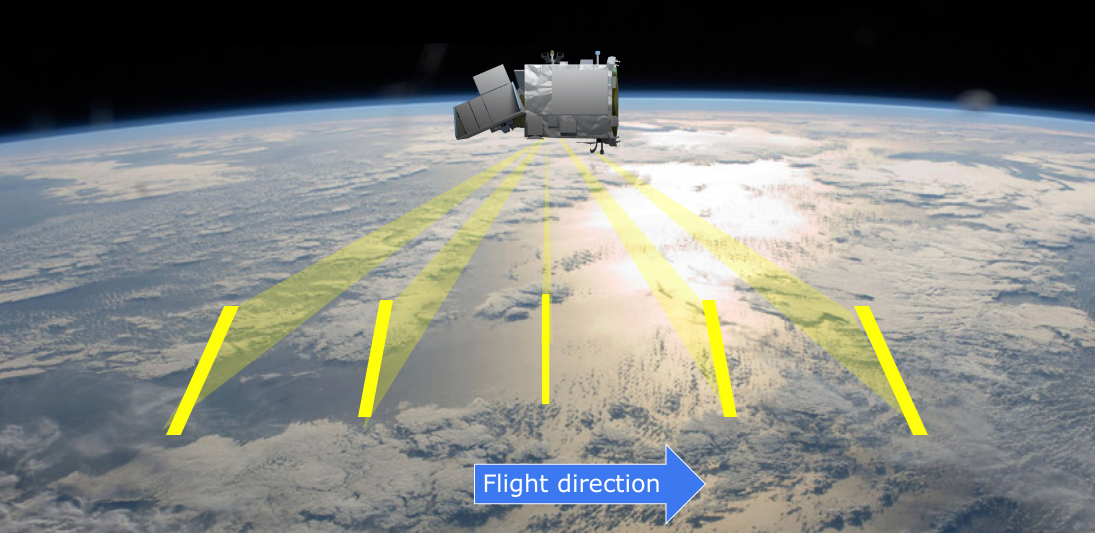
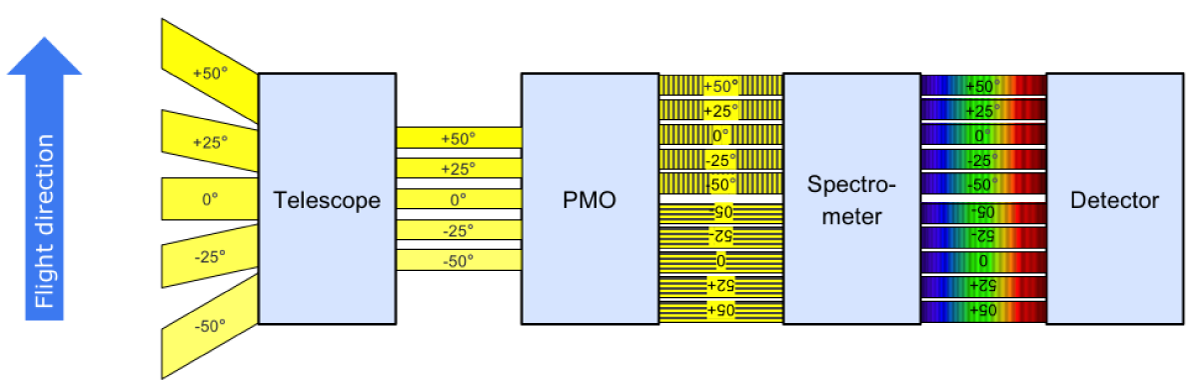
- A compact three-mirror segmented telescope assembly (patented by the consortium) to gather light from 0°, ±20° and ±50° (at satellite level) and direct the light towards a common entrance slit of a spectrometer.
- Polarization Modulation Optics (PMO) to encode the state of linear polarization in the intensity spectrum as a sinusoidal modulation.
- A compact and lightweight all-reflective imaging grating spectrometer.
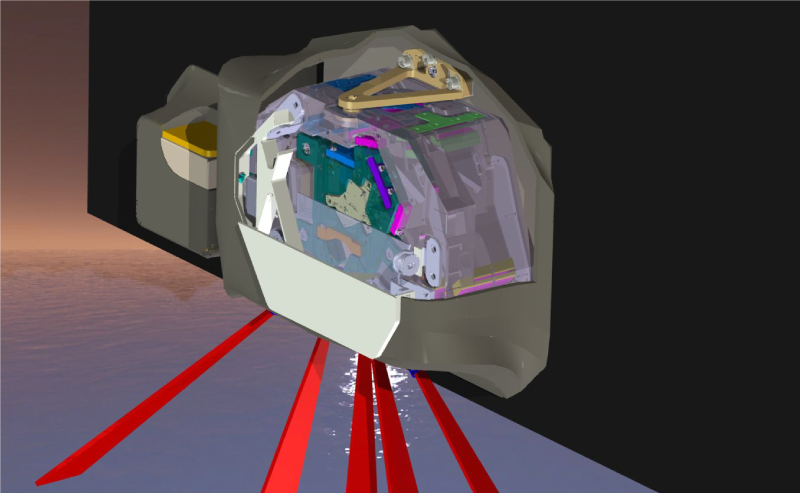
SPEXone multi-angle polarimeter instrument. First image: Artistic rendition of the polarimeter operating in space. Second image: Building blocks along the signal path: 1) five-viewing angle telescope assembly receiving light from the Earth atmosphere at angles of (50°, 20°, 0°, -20°, -50°) at the spacecraft, 2) polarization modulation optics module projecting the light on two orthogonal polarization directions (horizontal and vertical dash), 3) spectrometer module that creates a spectrum for each viewing direction and polarization direction 4) detector module that records the ten spectrally modulated spectra. Credit: SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research.
SPEXone Heritage
For the polarization modulation technique, SPEXone is based on heritage in ground-based and airborne applications. The spectral modulation technique was invented by Frans Snik and Christoph Keller at Leiden University and has been further developed in the Netherlands through several national programs.Major steps in this development have been the development, characterization, and field-testing (ground-based) of a SPEX Prototype (originally designed for a Mars orbiter) and the "upgrade" of the SPEX prototype into a stand-alone instrument, SPEX airborne, for operating on the high-altitude (21 km or 13 mi) NASA ER-2 research aircraft.
The spectrometer of SPEXone is based on Dutch heritage with the Sentinel-5 precursor Tropomi instrument, its predecessor OMI, and the derived compact version Spectrolite.